On Might 3, China launched its “complicated and bold” Chang’e-6 area mission, which, if profitable, would be the first ever to gather samples from the far facet of the moon. This mission, and different future “firsts” on the moon, Mars, and past are bolstering China’s plans to turn out to be a area superpower by 2045. There are already ample indicators that China is enacting insurance policies and making the required investments to take action. In April, Chinese language President Xi Jinping introduced probably the most in depth reorganization of the Folks’s Liberation Military (PLA) in a decade, with an emphasis on strengthening China’s army presence in area. And that in its 2022 white paper, Beijing outlined a spread of area insurance policies centered on defending China’s nationwide safety, incentivizing its industrial area trade, boosting innovation, and making developments in ventures equivalent to satellite tv for pc companies, area tourism, and useful resource extraction.
The steep enhance in its expenditures on area is one other clear indication of China’s ambitions: these expenditures mushroomed from C$3 billion in 2022 to C$19.5 billion in 2023. Though nonetheless trailing behind the U.S., which spent an estimated C$100 billion in 2023, China’s investments are displaying outcomes not solely in its state-led applications but additionally in its industrial program, which is driving advances in know-how, together with spacecraft design, propulsion programs, and robotics.
However China’s function within the quickly evolving and increasing international area panorama is inflicting trepidation amongst another spacefaring actors. Particularly, Beijing’s area program is a part of the broader realm of U.S.-China competitors, with clear diplomatic, army, and financial dimensions, together with considerations about China’s counter-space weapons, cybersecurity threats, and potential to take advantage of lunar sources. A part of this competitors includes forming partnerships with different established and rising area actors, together with Canada. Whether or not the U.S., China, and others can discover methods to work collectively in area whereas attempting to handle tensions of their relationships on Earth stays to be seen.
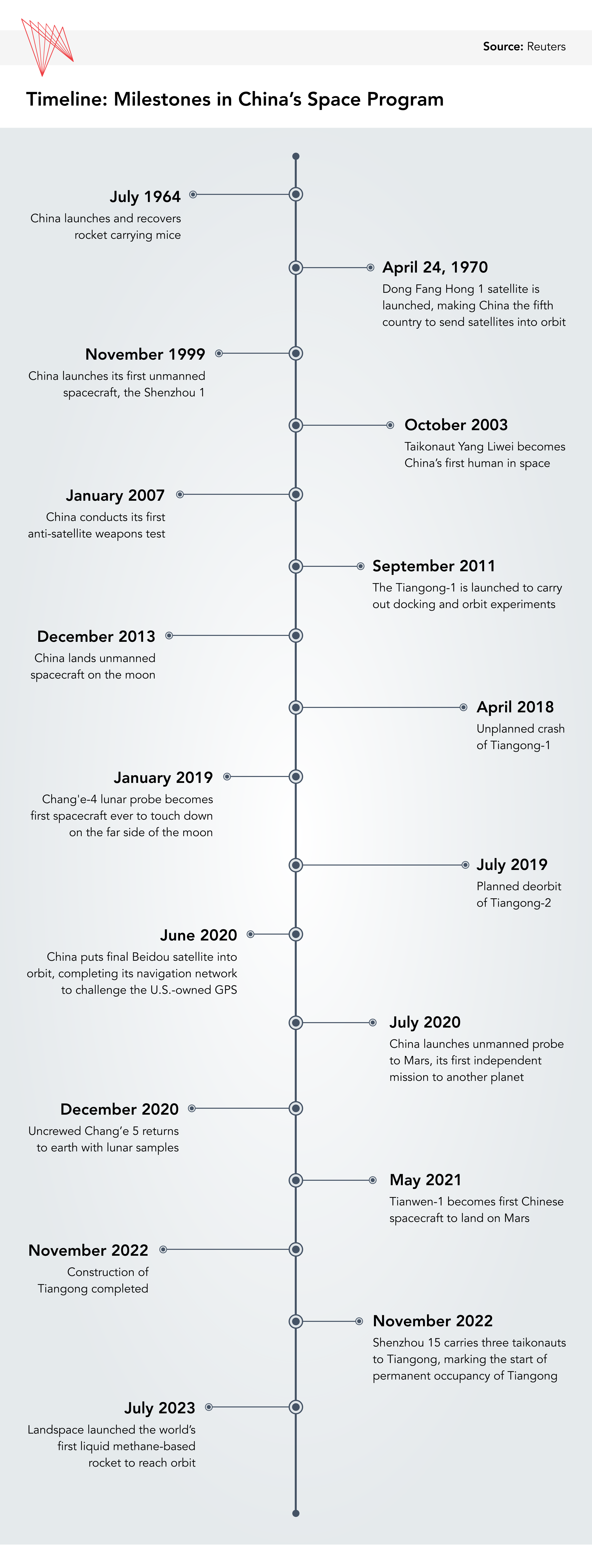
Historical past and milestones in China’s area program
China’s path to turning into an area energy is six a long time within the making, starting with its 1964 rocket launch and restoration. Six years later, in 1970, it grew to become solely the fifth nation (after the Soviet Union, the U.S., France, and Japan) to indigenously launch – that’s, with out counting on launch capacities from different area powers – a man-made satellite tv for pc, the Dong Fang Hong 1. Within the Nineteen Eighties, beneath then-leader Deng Xiaoping, China’s area program grew to become extra structured and was guided by a science and know-how growth program referred to as Challenge 863. This initiative fashioned the inspiration for the pivotal Challenge 921, also called the China Manned House Program, which, in 1992, articulated the nation’s goals of sending astronauts (also called ‘taikonauts’) to area and setting up an orbital area station. In 1993, Beijing established the nation’s nationwide area company, the China Nationwide House Administration (CNSA). This institutional help helped China launch its first unmanned spacecraft in 1999 and ship its first taikonaut into area in 2003.
In 2019, after a number of years of progress (see timeline beneath), China’s area program started to fulfill different spectacular milestones. That yr, it grew to become the primary nation to land on the far facet of the moon. In 2020, its Tianwen-1 mission landed its first rover on Mars. And by late 2022, China accomplished the development of the Tiangong House Station, with plans already underway for additional growth. These plans will quickly pay dividends: the Worldwide House Station is scheduled to be decommissioned in 2031, and when that occurs, the Tiangong would be the solely station in orbit. Within the meantime, by the top of the present decade, China plans to put astronauts on the moon; discover the outer photo voltaic system; and, by its Tianwen-4 mission scheduled to launch in 2029, discover one among Jupiter’s 95 moons (Callisto) and conduct a flyby of Uranus.
China’s industrial area sector

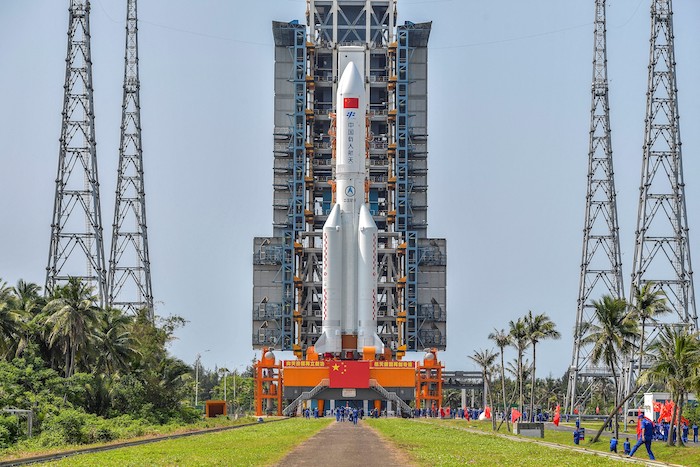
Along with monitoring the implications of the accomplishments described above, China’s companions and opponents are additionally maintaining a tally of the expansion of its industrial area sector. In 2023, 17 of China’s 67 rocket launches have been carried out by industrial area actors. In July 2023, LandSpace, one among China’s first industrial area firms, launched a methane-liquid oxygen area rocket, the primary of its variety.In 2024, the corporate’s website on Hainan Island will conduct its inaugural launch of the rocket. In early 2023, two different Chinese language firms – Hong Kong Aerospace Know-how Group and Touchroad – signed a memorandum of understanding (MOU) valued at greater than C$1.3 billion with the federal government of Djibouti to construct China’s first abroad spaceport in that nation. (Djibouti can be residence to China’s solely abroad naval base.) As a part of the MOU, the spaceport can be accomplished by 2027 and co-managed for 30 years earlier than being transferred to the Djibouti authorities.
Nonetheless, given the function of state-owned enterprises in China’s industrial sector, the road demarcating public from personal area enterprise is blurry, making it difficult to establish the magnitude of the latter. One instance is the state-owned China Satellite tv for pc Community Group. Mirroring U.S.-based SpaceX’s Starlink, this firm plans to launch as much as 26,000 satellite tv for pc parts of an web constellation globally between 2024 and 2029.
The private and non-private sectors are additionally entwined in China’s space-related infrastructure initiatives, together with the area element of the Belt and Highway Initiative (BRI). Additionally known as its “House Silk Highway,” this initiative contains satellites, navigation, and site positioning. China’s BeiDou satellite tv for pc navigation system, a substitute for GPS, has 45 satellites in orbit and 120 floor stations and is supposed to be the “digital glue” for China’s BRI infrastructure initiatives extending from East Africa to the South Pacific. This CNSA-led navigation system was initially developed for army functions, however is now operated in partnership with personal entities and different overseas governments for civilian use. It’s the world’s largest of its variety, and has achieved a degree of precision that has prompted concerns within the U.S. and the U.Ok., with London elevating questions about BeiDou’s potential to restrict the U.Ok.’s entry to area and to permit China to conduct surveillance of British residents. A lot of Beijing’s BRI companions, nevertheless, usually are not deterred and are more and more curious about accessing BeiDou’s companies for all the things from civilian navigation to missile monitoring.
On the subnational degree, Chinese language cities and provinces are different gamers in China’s area sector. The Beijing municipal authorities’s five-year motion plan, which commences this yr, goals to foster native and worldwide innovation to nurture startups and different high-tech personal entities within the area sector. In 2023, the Shanghai authorities additionally launched an motion plan for its industrial area sector, and the province of Shandong has articulated comparable targets for 2030 and 2035.
China’s function in international area governance and its increasing worldwide partnerships
This more and more dense internet of state and personal area actors will determine into the function China will play on the worldwide degree. Among the many ambitions articulated in Beijing’s 2022 white paper is the need for the nation to turn out to be a frontrunner in creating a extra sturdy worldwide framework for area governance by its lively participation in worldwide rule-making and the formulation of its personal nationwide area legislation. Over the previous eight years, China has signed at the least 46 agreements with 19 international locations and 4 worldwide organizations to advertise international area co-operation. In 2016, China signed an MOU with the UN Workplace for Outer House Affairs (UNOOSA) to increase using Tiangong to all UN member states. In April 2024, the director of UNOOSA recommended China’s collaborative efforts on the Tiangong House Station, referring to those efforts as a profit to all humankind.
This sort of worldwide collaboration has earned Beijing appreciable diplomatic goodwill. For instance, working with UNOOSA, China collaborates with newer area actors like Saudi Arabia to conduct experiments in area from Tiangong. It has additionally welcomed different Gulf Cooperation Council international locations to take part in joint missions aboard its area station and “financed, constructed, and launched” satellites for international locations with which it has shut relationships – together with Laos and Pakistan – as a part of a delivery-in-orbit contract whereby China each sells and launches satellites on their behalf. This association permits China to compete in a market that has lengthy been dominated by the U.S.
China has additionally partnered intently with Russia, a serious, albeit declining, area energy. The Worldwide Lunar Analysis Station (ILRS) is a China-Russia joint initiative to assemble a base on the south pole of the moon. The plan is that by 2050, the ILRS can be absolutely operational for lunar analysis and its lunar launch pads will help crewed interplanetary missions. Ten international locations have signed on to take part within the ILRS: Azerbaijan, Belarus, China, Egypt, Pakistan, Russia, South Africa, Thailand, Turkey, and Venezuela.
This rising partnership across the ILRS is seen as a competitor to the U.S.-led Artemis Accords. These non-binding Accords reinforce the provisions within the 1967 Outer House Treaty based mostly on the U.S.’s interpretations of useful resource extraction permitted beneath the treaty. Thirty-nine states have signed on to the Accords, together with India and a number of other shut U.S. allies, together with Canada and South Korea. Nonetheless, a few of these identical international locations – France, Germany, India, and Japan – have additionally joined China on initiatives associated to the ultimate module of its Tiangong area station.
Rising China-U.S. competitors in rising area race
A notable exception to China’s increasing listing of space-related companions is america. China isn’t a part of a number of key worldwide partnerships, equivalent to on the Worldwide House Station and Artemis missions, primarily due to Washington’s objections. The U.S. Congress, beneath the Wolf Modification (2011), prohibits NASA from utilizing federal funds to interact bilaterally with China on area co-operation. As well as, as a part of its Worldwide Site visitors in Arms Laws, the U.S. additionally restricts the export of satellite tv for pc components to China if it believes such exports might pose a army menace.
Throughout a current U.S. congressional listening to, the pinnacle of NASA, Invoice Nelson, said that China’s “civilian area program is a army program.” And in its 2023 report, the United States’ Workplace of the Director of Nationwide Intelligence (ODNI) described China’s area sector as a menace to U.S. safety. It highlighted the nation’s aspiration to outcompete the U.S. by 2045, which might “erode U.S. affect throughout army, know-how, financial, and diplomatic spheres.” Its major concern – and one of many components that motivated the congressional ban – is the function performed by the PLA in areas equivalent to navigation and satellite tv for pc reconnaissance. Of the greater than 700 satellites China has positioned in orbit, 245 are for army functions. (As compared, India has solely 26 army satellites out of greater than 120.) In the meantime, floor stations, except for satellite tv for pc monitoring and communication, can be utilized to infringe on private privateness, jam satellites, and observe overseas surveillance belongings and missile launches.
Washington’s allies have additionally cancelled contracts with China over safety considerations. In 2020, the Swedish House Company (SSC) determined to not renew contracts for a Chinese language floor station in Kiruna, Sweden, attributable to considerations that the information gathered on the station may very well be used for army intelligence, which might violate the SSC’s phrases of use. That very same yr, the SSC determined to not renew different contracts with China at floor stations in Australia and Chile. House collaboration between CNSA and the European House Company (ESA) has additionally been impacted by these considerations; European astronauts have been anticipated to go to Tiangong by 2022, however these plans have been suspended by the ESA, though the CNSA and ESA beforehand collaborated on a number of fronts, together with on lunar and deep area exploration. ESA director Josef Aschbacher gave an absence of “budgetary and political” approvals as the explanation for the halt on collaboration with China. The ESA’s 22 member states will as a substitute give attention to the Worldwide House Station. The Worldwide House Station was constructed and is maintained by 5 area businesses: the ESA, NASA, the Canadian House Company (CSA), the Japan Aerospace Exploration Company (JAXA), and Roscosmos (from Russia).

Canada, an Artemis accomplice and Worldwide House Station member, can be absent from China’s rising community of collaboration. Ottawa has considerations over Chinese language interference within the Canadian area sector. In 2021, a CSA engineer was accused of performing as a intermediary for Chinese language agency Spacety. Although acquitted of breach of belief, the engineer nonetheless faces disciplinary measures. As well as, in January 2024, the Canadian authorities launched a listing of delicate analysis areas and establishments, together with some in China, that would pose a danger to Canada’s nationwide safety. Amongst these on the listing are the North China Institute of Aerospace Engineering and China’s House Engineering College. Canadian researchers working in these delicate analysis areas could also be unable to entry federal grants with out certifying that they don’t seem to be working with or receiving funds from these or different establishments on the listing – probably impacting collaborative analysis efforts.
The perils and pitfalls of unmanaged competitors
Whereas competitors in area could also be unavoidable, how that competitors unfolds can nonetheless be managed. Unmanaged competitors carries profound dangers, such because the menace to infrastructure – and the planet beneath – in Earth’s more and more overcrowded orbit. In 2022, as an example, two SpaceX Starlink satellites almost collided with the crewed Tiangong, with the latter having to take emergency measures. China submitted a diplomatic be aware to the UN notifying it of the close to collision. Given that almost half of the objects in Earth’s orbit belong to the U.S. and its personal entities, and the rising danger of collision with China’s satellites, constructive and open dialogue between the 2 international locations is critical to make sure the protection of Earth’s close to orbit.
For now, the U.S. and its allies and China are caught in a safety dilemma in area – the place both sides is build up its army defences in response to the uncertainty over the opposite’s actions. However working in an setting as “chilly, darkish, and harmful” as area makes collaboration virtually a necessity given the sheer prices and dangers concerned.
A slender window of alternative for collaboration
Beijing has expressed its willingness to collaborate with the U.S. regardless of the latter’s safety considerations. The China Nationwide House Administration has repeatedly referenced the Wolf Modification as an impediment to potential co-operation with the U.S. in area. For NASA to work with China’s CNSA, the U.S. Federal Bureau of Investigation should certify that there isn’t any danger of know-how switch or violations of human rights in any collaborative endeavour. In truth, in a uncommon transfer, in December 2023, NASA offered the U.S. Congress with such a certification to acquire lunar samples acquired by China’s Chang’e-5 for analysis functions. The Chang’e-5 lunar samples, estimated to be roughly two billion years outdated, are anticipated to offer scientists distinctive insights into the origins and composition of the moon. China has prolonged an invite to researchers globally to entry samples for analysis functions, an motion China states is according to its purpose of exploring and creating area peacefully whereas participating in worldwide co-operation.
Worldwide co-operation in area, a world commons, not solely reduces the prices and dangers for collaborating nations however may ship “diplomatic utility,” significantly the place co-operation has not been the norm. The U.S. and Russia/Soviet Union have co-operated on a number of area efforts, together with the Chilly Conflict-era Apollo-Soyuz venture for testing a world area rescue, with a profitable drill accomplished in 1975. Regardless of tensions over Russia’s warfare in Ukraine, Russia and the U.S. proceed to work collectively on the Worldwide House Station. In March, SpaceX’s Falcon 9 rocket transported three American astronauts and one Russian cosmonaut to the Worldwide House Station as a part of the six-month-long Crew-8 mission that can conduct greater than 200 scientific experiments.
This U.S. and Russia/Soviet Union co-operation, which was essential and yielded quite a few advantages, gives a mannequin for potential U.S.-China co-operation. Such a mannequin of collaboration with China should take into account the present state of know-how that comes with larger army and cybersecurity safety threats. However the two international locations might work on co-operating in areas of decrease army menace, equivalent to deep area exploration.
What’s subsequent for China’s celestial ambitions?
China’s spectacular technological achievements and future ambitions in area are being bolstered by its rising affect and makes an attempt at displaying management in worldwide co-operation. Beijing’s nationwide area program and its booming industrial area trade are propelling the nation to the pinnacle of the pack of the world’s main spacefaring nations.
Whereas it spearheads its personal nationwide area program, China can be eager to create a repute as a collaborative state that upholds the worldwide rules-based order in area. The U.S. and its allies are skeptical of this, and a brand new area race stays an actual chance – with some saying it’s already on.
• Editors: Vina Nadjibulla, Vice-President Analysis & Technique, APF Canada; Erin Williams, Senior Program Supervisor, Asia Competencies, APF Canada.
Additionally on this sequence: For an summary of worldwide and Asian area applications, please see the introduction to this sequence. Our subsequent report will give attention to India, adopted by further experiences on Japan, South Korea, and Canada.