Whereas the icy moons of Jupiter and Saturn comprise water, Mars stays dry. Regardless of dozens of area missions, the Purple Planet has but to supply convincing proof that it conceals important water reserves beneath its floor.
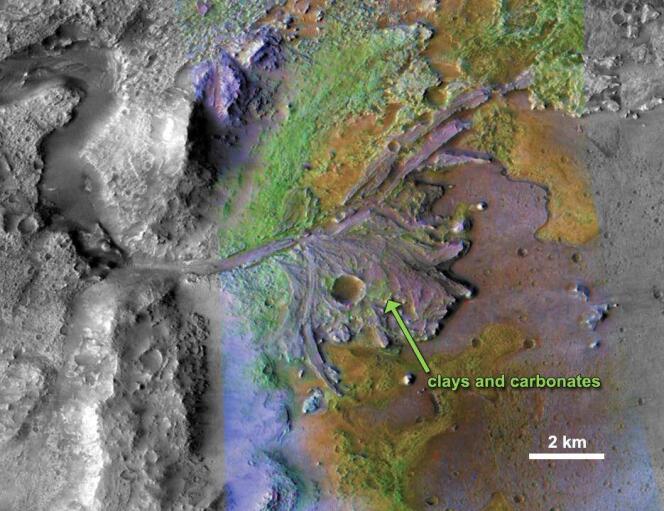
But Earth’s little cousin hasn’t all the time been so secretive. Varied research have proven that just a little over 4 billion years in the past, it skilled a “watery” period when lakes, rivers and even perhaps oceans may keep themselves on its soil. Branching valleys and historical terrains wealthy in hydrated clays are proof of this blissful interval of abundance.
Subsequently, the lack of a part of the Martian ambiance led to a discount within the greenhouse impact adopted by a gradual disappearance of water. The query is how lengthy this course of lasted and beneath what circumstances. That is what the American Area Company’s (NASA) Curiosity and Perseverance spacecraft have been attempting to ascertain since their arrival in 2012 and 2021 within the Gale and Jezero craters. “Lakes occupied these depressions 3.5 or 3.6 billion years in the past,” defined Nicolas Mangold, Director of Analysis on the French Nationwide Centre for Scientific Analysis (CNRS) Laboratory of Planetology and Geosciences in Nantes. “By learning the sedimentary and clay deposits left by the previous and exploring the traditional river delta that fed the latter, the intention is to find out whether or not the local weather on the time was moist and chilly, or dry and sizzling. The Perseverance rover can also be gathering samples, to be introduced again to Earth as a part of the MSR mission [Mars Sample Return, NASA-European Space Agency (ESA)]. They need to present exact info.”
For the second, issues are hazy. If water has flowed on Mars, the place has it gone? Was it sucked up into area with the Martian ambiance or did a few of it stay on web site, buried underground? Many groups all over the world are working to seek out solutions by looking for clues to its presence aside from these provided by polar ice caps and glaciers.
Controversy amongst scientists
As water can’t stay in a liquid state for lengthy on the floor of Mars, these investigations usually encompass recognizing current traces of its passage utilizing devices positioned in orbit. This opens the best way to every kind of controversy about the right way to interpret observations of this world, whose morphology is radically totally different from that of Earth. “A few of these controversies, corresponding to these regarding gullies – ravines one or two kilometers lengthy, found by the a whole lot alongside sure landforms within the early 2000s – have lastly been settled,” mentioned Susan Conway, a CNRS researcher on the Laboratory of Planetology and Geosciences in Nantes. Her staff just lately demonstrated within the journal Nature Communications that seasonal deposits of dry ice clarify the phenomenon, and never water flows.
You’ve gotten 25.43% of this text left to learn. The remainder is for subscribers solely.