Each spring, an uncommon phenomenon happens on Mars: What appear like little black spiders begin swarming throughout the Purple Planet’s south pole.
In fact, these should not precise arachnids or any residing creature. The odd objects, in a area of Mars referred to as Inca Metropolis, come from a sequence of carbon dioxide fuel eruptions. Over winter, the temperature plummets to -123˚C — so chilly that just about all the pieces freezes, together with carbon dioxide.
The fuel turns into deposits of dry ice on the planet’s floor. As spring rolls round and the temperature warms, the dry ice sublimates straight right into a fuel because it does on Earth, lacking out the liquid stage altogether.
Throughout this course of, the strain under the floor begins to construct up. Ultimately, you get a mini-explosion. The carbon dioxide bursts via the ice on the Martian floor, carrying a lot of darkish mud. The mud and carbon dioxide create enormous geysers, spraying the particles into the air.
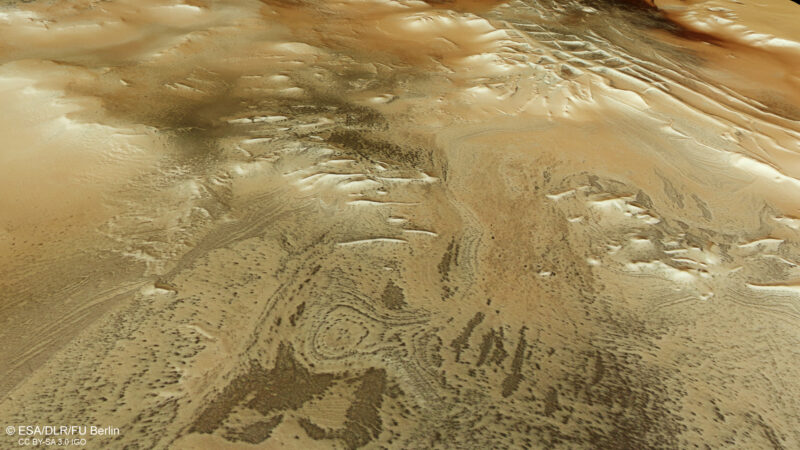
An outline of Mars’s Inca Metropolis. Photograph: European Area Company
Kilometer-wide ‘spiders’
Because it settles on the floor, the spidery shapes start to seem. All of them have an analogous look: an enormous darkish splotch within the center, with skinny leg-like spindles popping out of it. Although they appear tiny within the European Area Company (ESA) photographs, they’re really between 45m to 1,000m extensive.
Almost all “spiders” appeared within the Inca Metropolis. Formally generally known as the Angustus Labyrinthus, it earned its intriguing nickname as a result of the ridgelines look much like Inca formations on Earth. It was found in 1972, however nobody is aware of how the ridges fashioned. The ESA means that they might be “sand dunes turned to stone over time.”
The pictures of the spidery Inca Metropolis launched by the ESA date again to October 2020. This was the final southern spring on Mars. Although Mars has the identical 4 seasons we do, its seasons are double the size of ours right here on Earth.
At the moment, it’s autumn on the Martian south pole. The following spring equinox happens on November 12, 2024. At the moment, astronomers count on to see the area spiders bust from the floor once more.