Whereas we go about our every day lives on Earth, a nuclear-powered robotic the scale of a small automobile is trundling round Mars in search of fossils. In contrast to its predecessor Curiosity, Nasa’s Perseverance rover is explicitly meant to “seek for potential proof of previous life”, in keeping with the official mission goals.
Jezero Crater was chosen because the touchdown website largely as a result of it incorporates the remnants of historical muds and different sediments deposited the place a river discharged right into a lake greater than 3 billion years in the past. We don’t know if there was life in that lake, but when there was, Perseverance would possibly discover proof of it.
We will think about Perseverance coming throughout giant, well-preserved fossils of microbial colonies – maybe resembling the cabbage-like “stromatolites” that solar-powered micro organism produced alongside historical shorelines on Earth. Fossils like these can be large enough to see clearly with the rover’s cameras, and may also comprise chemical proof for historical life, which the rover’s spectroscopic devices may detect.
However even in such wildly optimistic eventualities, we wouldn’t be utterly certain we’d discovered fossils till we may see them beneath the microscope in laboratories on Earth. That’s as a result of it’s attainable for geological options produced by non-biological processes to resemble fossils. These are referred as pseudofossils. That’s why Perseverance isn’t simply in search of fossils in situ: it’s amassing samples. If all goes nicely, about 30 specimens shall be returned to Earth by a follow-on mission, which is being deliberate in collaboration with the European Area Company (Esa).
Earlier this month, Nasa introduced {that a} significantly intriguing pattern, the twenty fourth for Perseverance and informally named “Comet Geyser”, had joined the rover’s rising assortment. This one comes from an outcrop referred to as Bunsen Peak, a part of a rocky deposit referred to as the Margin Unit that’s near the crater’s edge.
This rock unit might have shaped alongside the shoreline of the traditional lake. Rover devices have proven that the Bunsen Peak pattern is dominated by carbonate minerals (the primary constituent of rocks like limestone, chalk and travertine on Earth).
The little carbonate grains are cemented along with pure silica (just like opal or quartz). Nasa’s press launch quotes Ken Farley, challenge scientist for Perseverance, saying: “That is the sort of rock we had hoped to seek out after we determined to research Jezero Crater.”
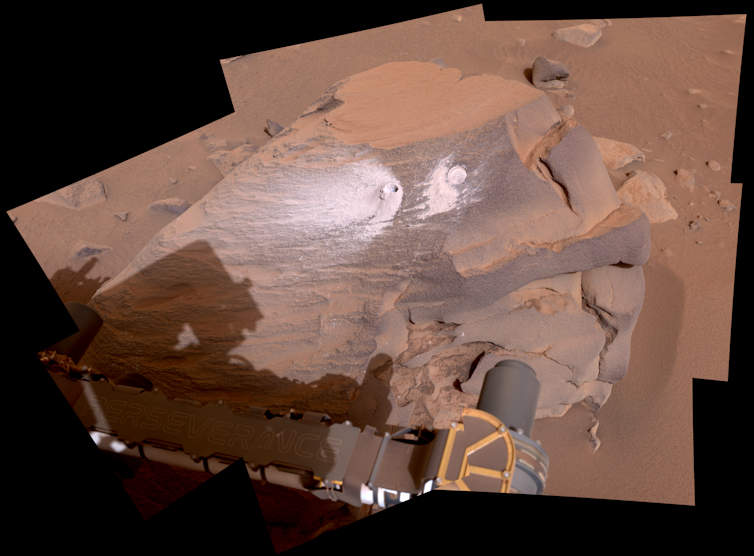
NASA/JPL-Caltech/ASU/MSSS
However what’s so particular about carbonates? And what makes the Bunsen Peak pattern significantly thrilling from the viewpoint of astrobiology, the examine of life within the Universe? Effectively, first, this rock might have shaped beneath circumstances that we’d recognise as liveable: capable of help the metabolism of life as we all know it.
One ingredient in habitability is the supply of water. Carbonate and silica minerals can each kind by direct precipitation from liquid water. Pattern 24 might have precipitated from the lake water beneath temperatures and chemical circumstances appropriate with life, though there could also be different potentialities that must be examined. In actual fact, carbonate minerals are puzzlingly uncommon on Mars, which has all the time had loads of CO₂ out there.
Within the moist environments of early Mars, that CO₂ ought to have dissolved in water and reacted to kind carbonate minerals. Evaluation of Bunsen Peak and of Pattern 24 when it’s despatched to Earth, might finally assist us clear up this thriller. One face of the outcrop has some attention-grabbing tough and streaky textures which may make clear its origins, however they’re onerous to interpret with out extra information.
Second, we all know from examples on Earth that historical sedimentary carbonates can yield great fossils. Such fossils embrace stromatolites composed of carbonate crystals precipitated immediately by micro organism. Perseverance hasn’t seen convincing examples of those.
There are some concentric round patterns within the Margin Unit however they’re virtually definitely an impact of weathering. Even the place stromatolites are absent, nevertheless, some historical carbonates on Earth comprise fossil colonies of microbial cells, which kind ghostly sculptures the place the unique mobile buildings have been changed by minerals.
The small grain measurement of the “Comet Geyser” pattern signifies a better potential to protect delicate fossils. Below some circumstances, fine-grained carbonates may even retain natural matter —- the modified stays of the fat, pigments and different compounds that make up residing issues. The silica cement makes such preservation extra doubtless: silica is usually more durable, extra inert, and fewer permeable than carbonate, and might shield fossil microbes and natural molecules inside rocks from chemical and bodily alteration over billions of years.
When my colleagues and I wrote a scientific paper referred to as A Discipline Information to Discovering Fossils on Mars in preparation for this mission, we explicitly really helpful sampling fine-grained, silica-cemented rocks for these causes. In fact, to crack open this pattern and discover its secrets and techniques, we have to carry it again to Earth.
An impartial assessment just lately criticised Nasa’s plans for the return of samples from Mars as too dangerous, too gradual, and too costly. Modified mission architectures at the moment are being evaluated to satisfy these challenges. Within the meantime, lots of of good scientists and engineers at Nasa’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory in California misplaced their jobs as a result of the US Congress successfully lowered funding for Mars pattern return by failing to commit the required degree of help.
Mars pattern return stays Nasa’s highest planetary science precedence and is strongly supported by the planetary science group world wide. The samples from Perseverance might revolutionise our view of life within the universe. Even when they don’t comprise fossils or biomolecules, they’ll gasoline many years of analysis and provides future generations a totally new view of Mars. Let’s hope Nasa and the US authorities can stay as much as the identify of their rover, and persevere.