SpaceX’s Starship May Save NASA’s Beleaguered Mars Pattern Return Mission
Dealing with budgetary strain for its Mars Pattern Return program, NASA has turned to personal trade for concepts—maybe with one particular firm in thoughts
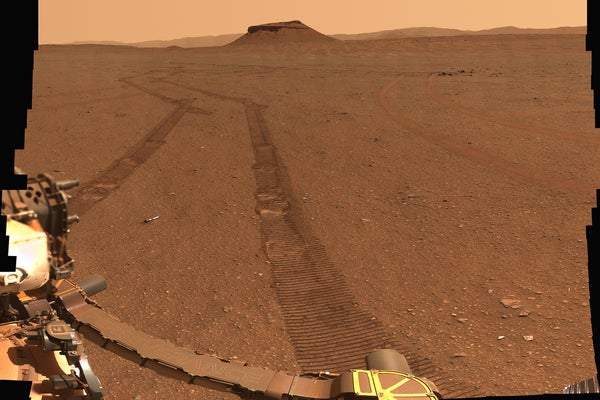

Ten tubes stuffed with valuable samples from Mars lurk on this panoramic vista, every cached on the planet’s floor by NASA’s Perseverance Rover for future retrieval. How and when these samples will return to Earth, nevertheless, stays unclear.
NASA/JPL-Caltech/ASU/MSSS
Don’t you hate it if you go away your valuables in your automobile with no option to get them again—they usually’re 140 million miles from Earth? That’s the prospect NASA is dealing with proper now. Its flagship multibillion-dollar mission to return invaluable and doubtlessly life-harboring samples of rock and dirt from Mars is in bother. The mission is dealing with an “unacceptable” rising value of $11 billion and a delay to 2040 for bringing the valuable payload residence, mentioned NASA chief Invoice Nelson in a name with reporters this week. That wait is “too lengthy,” he mentioned. As a substitute the company will now flip to personal corporations to supply it with modern designs to revive the mission. If they will achieve this, the prize would be the alternative to play a component in one of many grandest endeavors of our time, the hunt for habitability and maybe life on a neighboring world. “We’re so shut,” says Amy Williams, an astrobiologist on the College of Florida. “The scientific yield is nearly unimaginable.”
Mars Pattern Return (MSR), as this system is understood, was dreamed up practically three a long time in the past. The objective was to land a rover on Mars, gather samples of scientific curiosity from a location that might have hosted life and return them to Earth. The primary a part of the mission is underway, with the Perseverance rover presently trundling across the 28-mile-wide Jezero Crater, thought to have contained an historic lake that dried up 3.8 billion years in the past, with some two dozen samples in tow. The following part of the mission was imagined to have launched by 2031, gathering these samples from Perseverance and launching them again to Earth on a European-built spacecraft in 2033. In September 2023, nevertheless, an unbiased assessment discovered that objective was unachievable, given delays and value overruns in this system.
On April 15 NASA revealed a response that agreed with that evaluation. The company mentioned it wanted “out-of-the-box choices” to realize the objective of returning Perseverance’s samples to Earth. Its answer is “a shock,” says Casey Dreier, senior house coverage adviser for the Planetary Society. NASA is asking non-public corporations to place ahead concepts for methods to perform the mission at a decrease value and on a shorter timeframe. The company is looking for brief proposals by Might and can then decide this summer season on which concepts to hold ahead, with full proposals then anticipated by the autumn. “It’s added no certainty or clarification to the way forward for MSR,” Dreier says. “The outcomes of the inner research have been ‘let’s ask if anybody else has any concepts.’” That end result is “a bit disappointing,” he provides, given MSR was the highest precedence for the final two “decadal surveys” for planetary science. Such surveys are once-a-decade intergovernmental opinions that marshal communal enter to job NASA and different federal businesses with main scientific targets.
On supporting science journalism
When you’re having fun with this text, take into account supporting our award-winning journalism by subscribing. By buying a subscription you might be serving to to make sure the way forward for impactful tales concerning the discoveries and concepts shaping our world as we speak.
Jim Inexperienced, former chief scientist at NASA, who cemented MSR in his time as director of the company’s Planetary Science Division, says the state of affairs just isn’t wholly in contrast to the event of Europa Clipper, a mission to Jupiter’s moon Europa that NASA plans to launch in October. “We had in all probability a pair hundred million {dollars}’ value of research on Europa,” Inexperienced says. “We couldn’t come to closure.” Finally, nevertheless, NASA discovered a option to save prices by making Clipper a flyby mission, planning for it to zoom previous Europa dozens of occasions quite than enter into orbit across the moon, which is deep within the grip of Jupiter’s hardware-frying radiation belts. The same breakthrough may come for MSR. “Business has a chance to weigh in with some concepts,” Inexperienced says. “That is very wholesome. It’s precisely the method it should take to get a greater mission situation.”
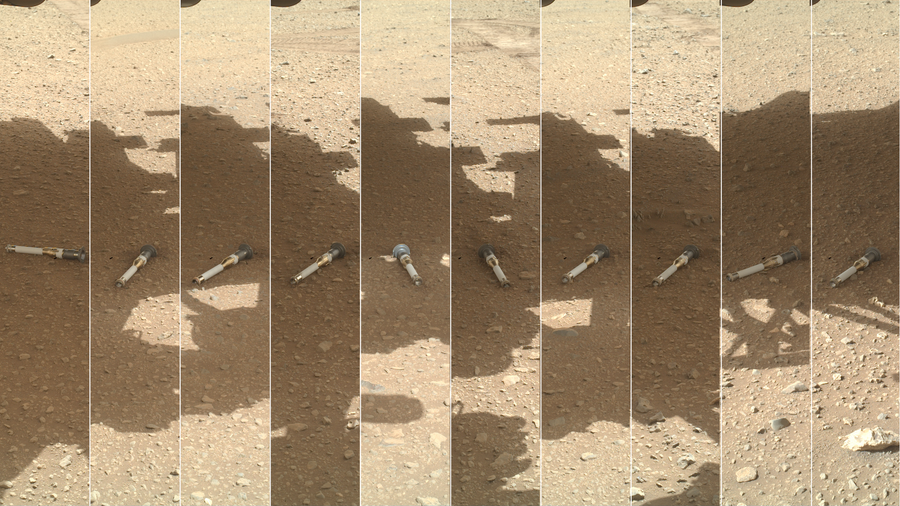
This photomontage exhibits a choice of pattern tubes cached by NASA’s Perseverance Mars rover on the “Three Forks” depot inside the mission’s touchdown website of Jezero Crater.
NASA may be soliciting concepts with one particular car in thoughts, Dreier says: SpaceX’s huge new Starship rocket. “It’s encouraging corporations to make use of infrastructure constructed for Artemis,” he says, referring to NASA’s huge effort to return astronauts to Earth’s moon. “The one conclusion you may actually draw from that’s they’re hoping Starship someway is the answer right here.” That would present MSR with a whopper of an answer. NASA is already funding Starship, the biggest rocket in historical past, to the tune of billions of {dollars} to ferry astronauts to the lunar floor—however Starship additionally has the potential to launch immense payloads off different worlds and again to Earth. “Starship has the potential to return critical tonnage from Mars inside [about] 5 years,” notice SpaceX CEO Elon Musk on X, previously Twitter, on April 15 in response to NASA’s MSR solicitation. Starship’s deliberate heavy-lift capabilities are so immense, the truth is, that the rocket may instantly simplify MSR. “You possibly can in all probability simply roll Perseverance into Starship and fly again to Earth,” Dreier says. Inexperienced thinks the concept of utilizing Starship for MSR is believable. “We have to leverage property that we didn’t have” when MSR was first devised, he says. SpaceX can also be hoping to in the end ship people to Mars within the coming a long time. “How are we going to study to launch people off the floor of Mars?” Inexperienced asks. MSR may present the opportune check mission.
One prospect seemingly taken off the desk by NASA is to make use of “Marscopters,” follow-ups to the wildly profitable Ingenuity helicopter that traveled to Mars with Perseverance. NASA says that “cautious analysis of Perseverance reliability” means such a car would not be needed to choose up samples from the rover. As a substitute Perseverance can be pushed again to the bottom of Jezero Crater in 2028, the place it might stay in a dormant “quiescent state” till the arrival of the MSR retrieval mission. Then the European House Company’s deliberate orbiting car would nonetheless launch “in 2030,” mentioned Sandra Connelly, NASA deputy affiliate administrator for science, at a city corridor assembly on April 15—presumably if an structure not involving Starship have been chosen—and the orbiter would gather the samples launched from the floor.
If an answer will be discovered, the scientific return on supply is nearly incalculable. Williams, a science workforce member on Perseverance, says the samples will enable us to exactly date the presence of water in Jezero Crater right down to thousands and thousands of years and to search for life’s potential imprints within the rocks of Mars in a method no rover alone can match. “You’ll be able to’t ship a synchrotron to Mars” to supply highly effective particle beams to finely parse samples, she says. “They’re like one mile in diameter.” Whereas it’s unclear exactly how far towards the query of life on Mars the samples would take us, they’d be a “sport changer” in our understanding of habitability on different worlds, Williams says. “These samples have the potential to revolutionize our understanding not simply of Mars however of all our internal rocky worlds and our seek for liveable worlds past our photo voltaic system,” she says.
Even with out the prospect of life, the samples will probably be scientifically astounding, says Jack Mustard, a planetary scientist at Brown College. Jezero Crater itself lies in a a lot bigger 1,200-mile-wide basin, known as Isidis Planitia, which can have resulted from a cataclysmic impression 3.9 billion years in the past. “There are elements of photo voltaic system evolution that may solely be accomplished by means of the return of samples [from Mars],” Mustard says. That features the formation of the planets themselves, the presence of magnetic fields on worlds corresponding to Earth—and as soon as Mars—and, specifically, the timing of big impacts within the early photo voltaic system. “Having datable samples from one other planetary physique to deal with that query can be unbelievable,” Mustard says. “Life is an attractive matter that will get all of the headlines. However at a extra lasting stage, it’ll be the questions on photo voltaic system evolution that the samples will reply that will probably be equally, if no more, essential.”