Japan’s MMX mission, scheduled to launch as quickly as September, is designed to return samples from the Martian moon Phobos that might decide its origins. (credit score: JAXA) |
by Ben Rider-Stokes
Tuesday, January 2, 2024
![]()
![]()
The 2 small moons of Mars, Phobos (about 22 kilometers in diameter) and Deimos (about 13 kilometers in diameter), have been puzzling scientists for many years, with their origin remaining a matter of debate. Some have proposed that they might be made up of residual particles produced from a planet or giant asteroid smashing into the floor of Mars (#TeamImpact). An opposing speculation (#TeamCapture), nonetheless, suggests the moons are asteroids that have been captured by Mars’s gravitational pull and have been trapped in orbit.
| Evaluating meteorites and materials introduced again from Phobos will probably be a improbable device for serving to us perceive the origin of the 2 moons. |
To resolve the thriller, we’ll want materials from the moons’ surfaces for analytical analyses on Earth. Fortunately, the Japan Aerospace Exploration Company (JAXA) will launch a mission, named Martian Moon eXploration (MMX), to Phobos and Deimos in September 2024. The mission will probably be carried by a newly designed rocket, the H3, which remains to be underneath growth after its first launch failed final March.
The spacecraft is anticipated to achieve Martian orbit in 2025, after which it should orbit Phobos and eventually accumulate materials from its floor earlier than returning to Earth by 2029.
It will make it the most recent in a collection of current missions bringing materials from house again to Earth, following on from JAXA’s profitable mission to asteroid Ryugu (Hayabusa2), in addition to NASA’s OSIRIS-REx mission to asteroid Bennu and China’s Chang’e 5 mission to the Moon.
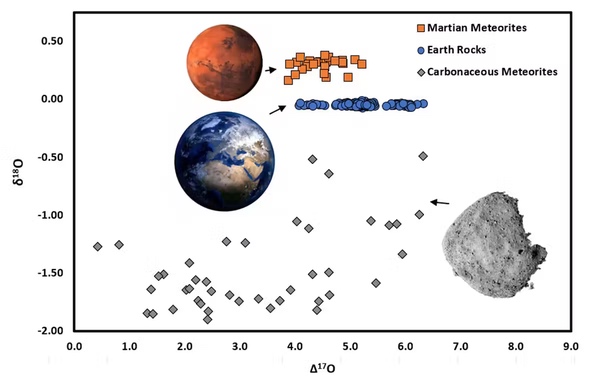
Oxygen isotope plot displaying the stark variations in oxygen between the Earth, Mars and asteroids. |
Giveaways
If an influence origin did certainly happen, we might anticipate finding related materials on Phobos to that which is discovered on Mars. Whereas we don’t have any materials returned straight from Mars (but), we’re fortunate sufficient to have rocks that has been ejected off its floor and ultimately discovered its option to Earth. These meteorites might subsequently be just like the fabric returned from Phobos, offering a improbable comparability.
Within the case of a captured asteroid origin, nonetheless, we usually tend to discover materials on Phobos that’s discovered on different asteroids in our Photo voltaic System. The prevailing speculation within the #TeamCapture group is that the moons are made up of the identical rock as many meteorites, referred to as carbonaceous chondrite. Fortunately, now we have loads of such meteorites and samples that we might evaluate with the Phobos materials.
Evaluating meteorites and materials introduced again from Phobos will probably be a improbable device for serving to us perceive the origin of the 2 moons. As soon as now we have materials within the laboratory, rigorous analytical strategies may be utilized to the samples.
One such approach is oxygen isotope evaluation. Isotopes are variations of parts whose nuclei have extra or fewer particles referred to as neutrons. Oxygen, for instance, has three steady isotopes, with atomic plenty of 16, 17, and 18.
| Samples returned from Phobos might present extraordinarily essential insights into the unique water content material of Mars, and a window to processes that occurred within the early Photo voltaic System. |
The sum of the isotopic ratios of oxygen-17/oxygen-16 and oxygen-18/oxygen-16 is denoted as Δ17O and is attribute of particular father or mother objects. Relying on the place within the Photo voltaic System a rocky physique is shaped, a definite oxygen composition is acquired and retained within the rocks. For instance, rocks from Earth have Δ17O of round 0, whereas meteorites from Mars have Δ17O of round 0.3. Due to this fact, rocks from Earth and Martian meteorites may be readily separated from each other.
If Phobos shaped in the identical or no less than related location within the Photo voltaic System to Mars, we might anticipate the composition of the fabric introduced again by MMX additionally to have Δ17O of round 0.3.
As talked about beforehand, #TeamCapture recommend a carbonaceous chondrite-like origin for Phobos. All identified carbonaceous chondrites studied by scientists have revealed damaging isotopic Δ17O, starting from –0.5 all the way in which right down to –4. Oxygen can subsequently be an especially highly effective device in deciphering the origin of the moons of Mars and ought to be a excessive precedence for the mission as soon as materials is returned to Earth.
If Phobos does certainly characterize an historic fragment of Mars, it might comprise essentially the most primitive of Martian materials. Mars has skilled a variety of processes which have altered the rocks on its floor, together with wind erosion and water alteration. Primarily based on options akin to dry riverbeds noticed from orbiters akin to Viking, it’s clear that water on Mars as soon as existed.
This water seemingly originated from a mixture of asteroids and comets, and volcanic exercise. Mars additionally retained a thick environment, which allowed water to be current as a liquid on the planet’s floor.
Phobos, however, has remained an airless physique the place processes akin to contamination from water haven’t occurred (although minor influence occasions might have taken place.) Because of this samples returned from Phobos might present extraordinarily essential insights into the unique water content material of Mars, and a window to processes that occurred within the early Photo voltaic System.
MMX is among the most fun upcoming missions in house exploration. With lower than a yr to go, our fingers are already firmly crossed for a profitable launch, pattern acquisition, and pattern return. Many scientists, together with myself, would completely love the opportunity of in the future finding out these samples.
Be aware: we’re utilizing a brand new commenting system, which can require you to create a brand new account.